Non-wovens
Contents
Introduction
Nonwoven textiles are those which are neither woven nor knit, for example felt. General use hyphenates the word, but industrial use spells it as one word. Non-wovens are typically not strong (unless reinforced by a backing or densified). In the recent years non-woven material has become an alternative to polyurethane foam.
Non-woven fabric is typically manufactured by putting small fibers together in the form of a sheet (web) and then binding them either mechanically (as in the case of felt, by interlocking them with serrated needles such that the inter-fiber friction results in a stronger fabric), with an adhesive, or thermally {by applying binder(in the form of powder, paste, or polymer melt) and melting the binder onto the web by increasing temperature}.
Raw material
Non-woven materials are nowadays mainly produced from man-made fibers. Two synthetic polymers dominate the market: polypropylene and polyesters (mainly PET). Nonwovens are often application-designated as either durable or disposable. Nonwoven used as a housewrap to prevent water infiltration is a durable nonwoven. Nonwoven used as a facing on a baby diaper is a disposable or single-use nonwoven.
Application
Non-woven materials are used in numerous applications, including:
Hygiene
- Baby diapers
- Feminine hygiene
- Adult incontinence products
- Wipes
- Bandages and wound dressings
Medical
- Isolation gowns
- Surgical gowns
- Surgical drapes and covers
- Surgical scrub suits
- Caps
Technical
- Roll roofing and shingle reinforcement
- Insulation backing
- Battery electrode separators
- Vinyl flooring reinforcement
- Plastic surface reinforcement (veils)
- Wall coverings
- Honeycomb structural components
- Ceiling tile facings
- Circuit board reinforcement
- Electrical insulation
Geotextiles
- Soil stabilizers and roadway underlayment
- Agriculture mulch
- Pond and canal water barriers
- Sand infiltration barrier for drainage tile
Other
- Carpet backing (primary and secondary)
- Composites
- Marine sail laminates
- Table cover laminates
- Backing/Stabilizer for machine embroidery
- Thermal insulation (fiberglass quilting/batting)
- Pillows, cushions, and upholstery padding
- Batting in quilts or comforters
- Consumer and medical face masks
- Tarps, tenting and transportation (lumber, steel) wrapping
- Disposable clothing (foot coverings, coveralls)
Sample IP analysis
- Area: Baby diapers and Feminine hygiene.
- Search: Based on title, abstract and claims for some major companies in this field.
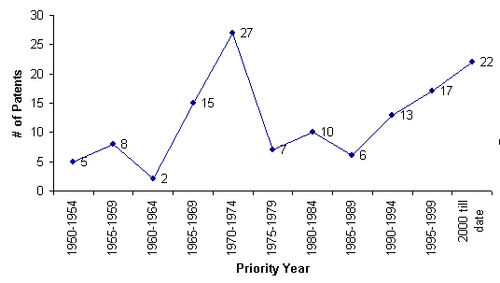
Year wise IP activity
- Based on title, abstract and claims for some major companies in this field.The graph is based on the patents of Kimberly-Clark Corp, Johnson & Johnson, Procter & Gamble, and Playtex from 1836 to 2006.
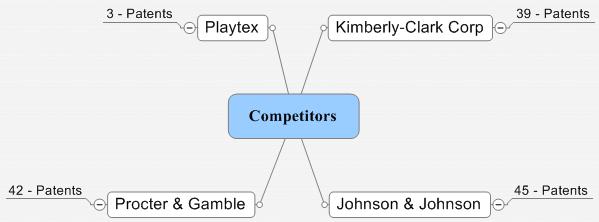
Competitive analysis
Sample analysis of some patents
- This information is according to analysis of 27 patents.
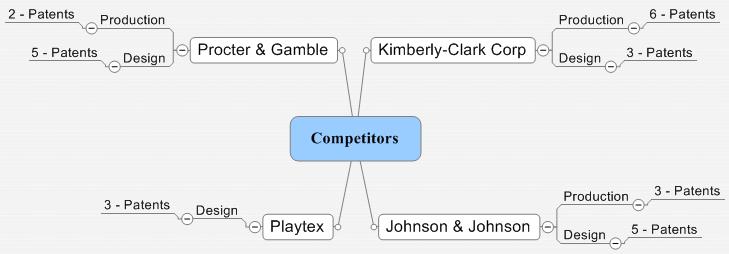
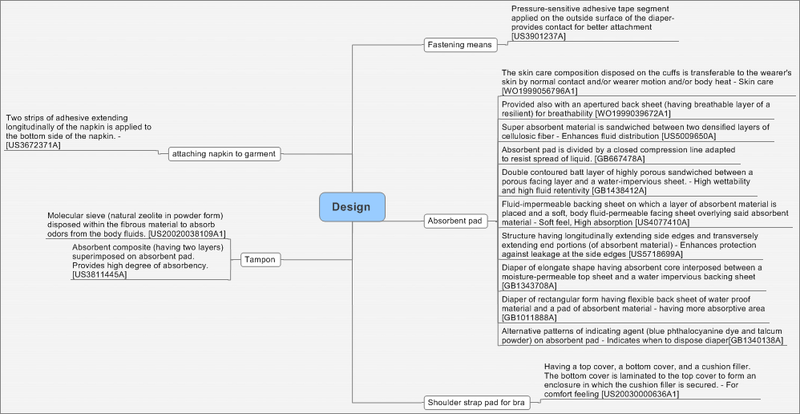
Design patents
- Classification of Design patents
| Design | Total records | Kimberly Clark | Procter & Gamble | Johnson & Johnson | Playtex |
| Absorbent pad | 11 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 0 |
| Attaching napkin to garment | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fastening means | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Shoulder strap pad for bra | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Tampon | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
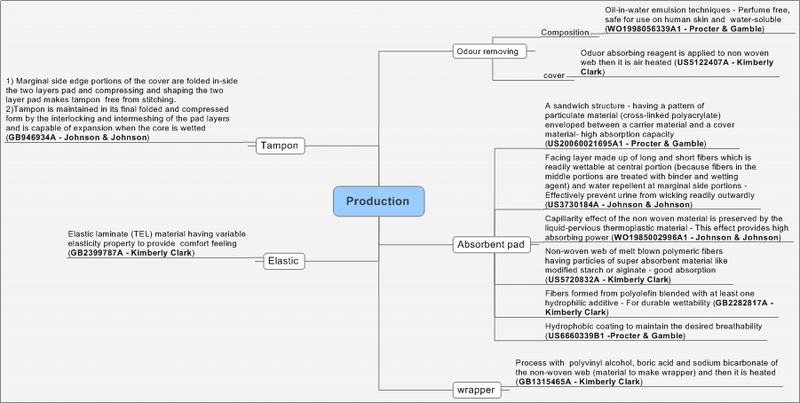
Production patents
- Classification of Production patents
| Production | Total records | Kimberly Clark | Procter & Gamble | Johnson & Johnson | Playtex |
| Absorbent pad | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Odour removing composition | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Wrapper | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Elastic | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tampon | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |