Femtocells
This report presents a brief summary about femtocells and also focuses on its various applications. A detailed taxonomy is presented which covers all the aspects related to femtocells. A detailed landscape analysis of patent and non-patent literature is done. The product information of major players in the market is also captured. The final section of the report also covers the existing and future market predictions.
Dolcera Landscape Procedure
- Background study - Background study is done with web search depending on the area of client interest.
- Finding key player/inventors - Web search is carried out to find the products and technologies of key players.
- Patents Search -
- Key patents search.
- Prepared search queries using keywords and classification and finalized these in Micropat/Thompson.
- Patents Classification - Classify all patents by creating taxonomy.
- Specific analysis as required by client like SWOT, SOA, PEST, Claim, and White Space analysis.
- Reporting -
- All necessary data are presented in format of wiki or in form of power point slides.
- Dashboard - Graphical representation of Patents classification.
Key Findings
- Qualcomm, Samsung and NEC are the major players in femtocells technology
- Key patents in the femtocells are held by Ericsson, Kineto Wireless and Qualcomm.
- Patenting activity has seen a very high growth rate in the last two years.
- US and WO are very active in femtocell technology research.
Contents
Introduction
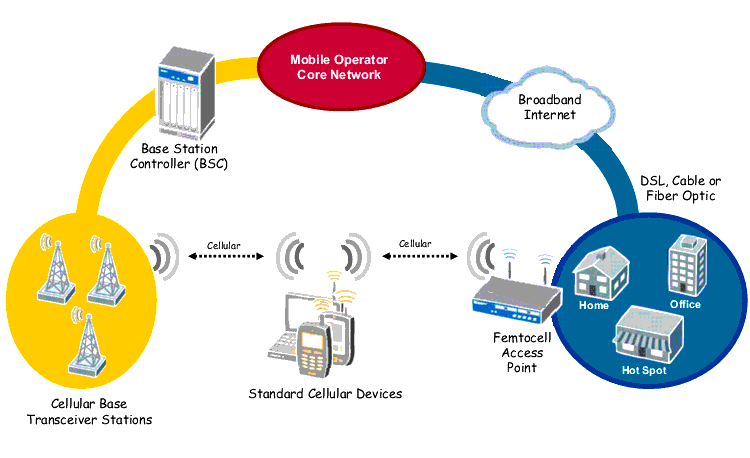
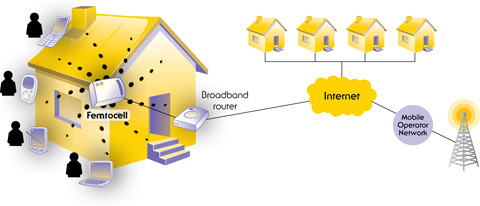
A femtocell is a small cellular base station designed for use in residential or small business environments. It connects to the service provider’s network via broadband (such as DSL or cable) and typically supports 2 to 5 mobile phones in a residential setting. A femtocell allows service providers to extend service coverage inside of your home - especially where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable - without the need for expensive cellular towers. It also decreases the backhaul costs since it routes your mobile phone traffic through the IP network. Source
A femtocell is sometimes referred to as a “home base station”, “access point base station”, “3G access point”, “small cellular base station” and “personal 2G-3G base station”.
Femtocells are low-power wireless access points that operate in licensed spectrum to connect standard mobile devices to a mobile operator’s network using residential DSL or cable broadband connections.
Read More?
Click on Femtocell Background to read more about Femtocell.
Taxonomy
- Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy
Femtocell - Search Strategy
Control Patents
Control patents are mostly used
- to prepare concepts
- to search classes, and
- to verify the search strategy
| S. No. | Patent/Publication No. | Publication Date (mm/dd/yy) | Assignee / Applicant | Title |
| 1 | US20110047011A1 | 02/24/11 | Motorola | Incentives to optimize the performance of femto cell groups |
| 2 | US20110039560A1 | 02/17/11 | Cisco Technology | System and method for providing access in a network environment |
| 3 | WO2011005654A2 | 01/13/11 | Intel Corporation | Initializing femtocells |
| 4 | US7855977B2 | 12/21/10 | AT&T | Alarming in a femto cell network |
| 5 | US20100309790A1 | 12/09/10 | Alcatel-Lucent | Femto base stations and methods for operating the same |
| 6 | US20100285812A1 | 11/11/10 | Hitachi | Call admission priority control determination device and mobile wireless communication system |
| 7 | US20100279704A1 | 11/04/10 | NEC Corporation | Method for controlling access to a mobile communications network |
| 8 | US20100267386A1 | 10/21/10 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for facilitating handoff between a femtocell base station and a cellular base station |
| 9 | US20100177695A1 | 07/15/10 | Samsung Electronics | Technique for interference mitigation using mobile station signaling |
| 10 | JP2010157807A | 07/15/10 | NEC Corporation | Communication system, femto cell base station, authentication device, communication method, and communication program |
| 11 | US20100165957A1 | 07/01/10 | Airvana | Providing a cellular network with connectivity to a different network |
| 12 | WO2010063227A1 | 06/10/10 | Huawei Technologies | Positioning method and device for the home base station |
| 13 | US20100135201A1 | 06/03/10 | AT&T | Registration notification for mobile device management |
| 14 | US20100130212A1 | 05/27/10 | ZTE | Femto cell handover in wireless communications |
| 15 | GB2461845A | 01/20/10 | Ubiquisys | Femtocell basestation scrambling code selection |
| 16 | US20090286540A1 | 11/19/09 | AT&T | Femtocell architecture for information management |
| 17 | EP2112854A1 | 10/28/09 | Nokia Siemens Networks | Access control method for cellular networks comprising femto-cells |
| 18 | US20090253421A1 | 10/08/09 | Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications | Local network management of femtocells |
| 19 | GB2456503A | 07/22/09 | ip.access | Using global cell identifier for handover in a combined femto-cell/macro-cell environment |
Patent Classes
| S. No. | Class Code | Class Type | Class Definition |
| 1 | 370328 | USPC | Multiplex communications - Communication over free space - Having a plurality of contiguous regions served by respective fixed stations |
| 2 | 370329 | USPC | Multiplex communications - Communication over free space - Having a plurality of contiguous regions served by respective fixed stations – Channel assignment |
| 3 | 370331 | USPC | Multiplex communications - Communication over free space - Having a plurality of contiguous regions served by respective fixed stations - Channel assignment – Hand-off control |
| 4 | 370338 | USPC | Multiplex communications - Communication over free space - Having a plurality of contiguous regions served by respective fixed stations – Contiguous regions interconnected by a local area network |
| 5 | 4554221 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system |
| 6 | 455434 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Control or access channel scanning |
| 7 | 4554351 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Registration |
| 8 | 4554352 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Registration – System selection |
| 9 | 4554353 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Registration - System selection – Based on priority |
| 10 | 455436 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Handoff |
| 11 | 455444 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Handoff – Between macro and micro cells |
| 12 | 455445 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Call routing |
| 13 | 455446 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Including cell planning or layout |
| 14 | 455450 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Channel allocation |
| 15 | 4554522 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system - Channel allocation - Dynamic allocation – Based on service quality |
| 16 | 4554561 | USPC | Telecommunications - Radiotelephone system - Zoned or cellular telephone system – Location monitoring |
| 17 | 455522 | USPC | Telecommunications - Transmitter and receiver at separate stations - Plural transmitters or receivers - To or from mobile station – Transmission power control technique |
| 18 | 455561 | USPC | Telecommunications - transmitter and receiver at same station - Radiotelephone equipment detail – Base station detail |
| 19 | H04B7* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Transmission - Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field |
| 20 | H04L001228 | IPC | Electric communication technique - Transmission of digital information - Data switching networks - characterised by path configuration, e.g. local area networks (LAN), wide area networks (WAN) |
| 21 | H04L001256 | IPC | Electric communication technique - Transmission of digital information - Data switching networks - Stored and forward switching systems - Packet switching systems |
| 22 | H04L002906 | IPC | Electric communication technique - Transmission of digital information - Arrangements, apparatus, circuits or systems, not covered by a single one of groups - Communication control; Communication processing - characterised by a protocol |
| 23 | H04W4* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Services or facilities specially adapted for wireless communication networks |
| 24 | H04W16* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures |
| 25 | H04W28* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Network traffic or resource management |
| 26 | H04W36* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Hand-off or reselecting arrangements |
| 27 | H04W40* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Communication routing or communication path finding |
| 28 | H04W48* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection |
| 29 | H04W60* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Registration, e.g. affiliation to network; De-registration, e.g. terminating affiliation |
| 30 | H04W68* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Notification of users, e.g. alerting for incoming communication or change of service |
| 31 | H04W72* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Local resource management, e.g. wireless traffic scheduling or selection or allocation of wireless resources |
| 32 | H04W88* | IPC | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices |
| 33 | H04W003638N | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Hand-off or reselecting arrangements - Reselection control - by fixed network equipment - Of the core network |
| 34 | H04W003600P6R | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Hand-off or reselecting arrangements - Control or signalling for completing the hand-off - Transmission and use of information for re-establishing the radio link - Of resource information of target access point |
| 35 | H04W003600P6T | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Hand-off or reselecting arrangements - Control or signalling for completing the hand-off - Transmission and use of information for re-establishing the radio link - of access information of target access point |
| 36 | H04W007204F | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Local resource management, e.g. wireless traffic scheduling or selection or allocation of wireless resources - Wireless resource selection or allocation – Control information exchange between nodes |
| 37 | H04W008404C2 | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Network topologies - Hierarchical pre-organized networks, e.g. paging networks, cellular networks, WLAN or WLL - Large scale networks; Deep hierarchical networks - Public Land Mobile systems, e.g. cellular systems - using private Base Stations, e.g. femto Base Stations |
| 38 | H04W000824N | ECLA | Electric communication technique - Wireless communication networks - Network data management - Processing or transfer of terminal data, e.g. status or physical capabilities - Transfer of terminal data – From a network towards a terminal |
Concept Table
English Keywords
| S. No. | Concept-1 | Concept-2 | Concept-3 |
| Femtocell | Access point | Gateway | |
| 1 | femtocell | access point | gateway |
| 2 | femto cell | access terminal | home gateway |
| 3 | home base station | 3g access point | security gateway (segw) |
| 4 | small cellular base station | access point base station | |
| 5 | personal 2g-3g base station | low power wireless access points | |
| 6 | femto base station | miniature cellphone access points | |
| 7 | femto network | miniature cell phone access points | |
| 8 | femtocell access point (fap) | ||
| 9 | cellular network access points |
French Keywords
| S. No. | Concept-1 | Concept-2 | Concept-3 |
| Femtocell | Point d’accès | Gateway | |
| 1 | femtocell | point d’accès | gateway |
| 2 | cellules femto | terminal d’accès | accueil passerelle |
| 3 | station de base home | point d’accès 3g | security gateway (segw) |
| 4 | petite station de base cellulaire | accès station de point de base | |
| 5 | personnel de station de base 2g-3g | low power points d’accès sans fil | |
| 6 | station de base femto | miniature points d’accès cellulaire | |
| 7 | miniature points d’accès de téléphonie cellulaire | ||
| 8 | point d’accès femtocell (fap) | ||
| 9 | points d’accès au réseau cellulaire |
German Keywords
| S. No. | Concept-1 | Concept-2 | Concept-3 |
| Femtocell | Access Point | Gateway | |
| 1 | femtocell | access point | gateway |
| 2 | femto-zelle | access terminal | home-gateway |
| 3 | home basisstation | 3g access point | security gateway (segw) |
| 4 | kleine zelluläre basisstation | access point basisstation | |
| 5 | persönliche 2g-3g-basisstation | low-power-wireless access points | |
| 6 | femto-basisstation | miniatur-handy-zugangspunkte | |
| 7 | miniatur-handy-zugangspunkte | ||
| 8 | femtocell access point (fap) | ||
| 9 | cellular network access points |
Search Query
Database: Micropat
Databases covered: USG USA EPA EPB WO JP DEG DEA DET DEU GBA FRA
Years searched: 1836 - 8th March 2011
| S. No. | Concept | Scope | Query | No. of Hits |
| 1 | Femtocell (Narrow keywords) | Full patent spec. | femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR (femto NEAR base NEAR station) OR (femto NEAR3 network*1) | 3795 |
| 2 | Femtocell (Broad keywords) | Claims, Title or Abstract | femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR (home NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (access NEAR5 point NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (small NEAR5 cellular NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (personal NEAR5 "2g-3g" NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1) | 3176 |
| 3 | Assignees Search (Restricted with Keywords) | Assignee/Applicant | Qualcomm OR Intel OR Picochip OR Ericsson OR ip.access OR (ip ADJ access) OR (Nokia ADJ Siemens) OR Motorola OR ZTE OR Agilent OR NEC OR Ubiquisys OR (AirWalk ADJ Communications) OR (Alcatel ADJ Lucent) OR Hitachi OR Cisco OR Airvana OR (Tatara ADJ System*1) OR Vodafone OR AT&T OR (Sprint ADJ Nextel) OR Verizon OR (Mobile ADJ TeleSystem*1) | 2145 |
| Full patent spec. | (((access ADJ point*1) OR (access NEAR5 terminal*1) OR (3g NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR (access NEAR5 point*1 NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR (low NEAR5 power NEAR5 wireless NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR (miniature NEAR5 (cellphone OR (cell ADJ phone)) NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR ((femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1)) NEAR5 access point) OR fap OR (cellular NEAR5 network NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1)) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1) OR femto*1)) OR (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1) OR femto*1) OR ((gateway OR (home ADJ gateway) OR (security ADJ gateway) OR segw) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1) OR femto*1)) (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1) OR femto*) | |||
| 4 | Access Points Keywords with Femtocell | Claims, Title or Abstract | ((access ADJ point*1) OR (access NEAR5 terminal*1) OR (3g NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR (access NEAR5 point*1 NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR (low NEAR5 power NEAR5 wireless NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR (miniature NEAR5 (cellphone OR (cell ADJ phone)) NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1) OR ((femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1)) NEAR5 access point) OR fap OR (cellular NEAR5 network NEAR5 access NEAR5 point*1)) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR (home NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (access NEAR5 point NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (small NEAR5 cellular NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (personal NEAR5 "2g-3g" NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1)) | 1191 |
| 5 | Gateway Keywords with Femtocell | Claims, Title or Abstract | (gateway OR (home ADJ gateway) OR (security ADJ gateway) OR segw) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR (home NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (access NEAR5 point NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (small NEAR5 cellular NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR (personal NEAR5 "2g-3g" NEAR5 base NEAR5 station*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1)) | 359 |
| 6 | Classification Search (Restricted with Keywords) | Any Classification | 370328 OR 370329 OR 370331 OR 370338 OR 4554221 OR 455434 OR 4554351 OR 4554352 OR 4554353 OR 455436 OR 455444 OR 455445 OR 455446 OR 455450 OR 4554522 OR 4554561 OR 455522 OR 455561 OR H04B7* OR H04L001228 OR H04L001256 OR H04L002906 OR H04W4* OR H04W16* OR H04W28* OR H04W36* OR H04W40* OR H04W48* OR H04W60* OR H04W68* OR H04W72* OR H04W88* OR H04W003638N OR H04W003600P6R OR H04W003600P6T OR H04W007204F OR H04W008404C2 OR H04W000824N | 1212 |
| Full patent spec. | (((access ADJ point*1) OR (access NEAR terminal*1) OR (3g NEAR access NEAR point*1) OR (access NEAR point*1 NEAR base NEAR station) OR (low NEAR power NEAR wireless NEAR access NEAR point*1) OR (miniature NEAR (cellphone OR (cell ADJ phone)) NEAR access NEAR point*1) OR ((femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1)) NEAR access point) OR fap OR (cellular NEAR network NEAR access NEAR point*1)) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1))) OR (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1)) OR ((gateway OR (home ADJ gateway) OR (security ADJ gateway) OR segw) AND (femtocell*1 OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 base NEAR5 station) OR ((femto OR (femto ADJ cell*1) OR femtocell*1) NEAR5 network*1))) | |||
| 7 | Combined Query | 1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4 OR 5 OR 6 | 2990 Unique families (5694) |
Taxonomy
- Use the mouse(click and drag/scroll up or down/click on nodes) to explore nodes in the detailed taxonomy
- Click on the red arrow adjacent to the node name to view the content for that particular node in the dashboard
Sample Analysis
Patent Analysis
| S.No. | Patent/Publication No. | Title | Dolcera Analysis | |
| Problem | Solution | |||
| 1 | US20110047011A1 | Incentives to optimize the performance of femto cell groups | The convergence of wireless communication and mobile computing devices continues to spur demand for wireless broadband communication services. As the demand grows, so too must the network infrastructure needed to support wireless communications. | Method of incentivizing an operator of femto cell infrastructure to efficiently utilize the femto cell infrastructure. The method can include establishing, for an end user device, telecommunication network presence on a femto cell. At least one parameter measured within the femto cell can be received. Based on the measured parameter, a determination can be made as to whether to award at least one incentive to the operator of the femto cell, and the incentive can be awarded to the operator. |
| 2 | US20110039560A1 | System and method for providing access in a network environment | Networking architectures have grown increasingly complex in communication environments. Femtocells have gained recent notoriety due to their capabilities. For many femto scenarios, connectivity and/or access protocols can pose a number of problems for end users. | A method includes evaluating geolocation information associated with a mobile node and using the geolocation information to identify a femtocell capable of providing network access to the mobile node. A primary scrambling code is provided to the mobile node for operation in an idle mode. The method also includes communicating a secondary scrambling code to initiate access to the femtocell by the mobile node when operating in an active mode. |
| 3 | WO2011005654A2 | Initializing femtocells | Femto access points generally cannot be initiated into an operator’s network, such as a WiMAX network. | The femtocell may be pre-provisioned with certain credentials so that a femtocell access point can authenticate itself to the operator’s network and become attached to that network. The pre-provisioned parameters may include non-operator specific parameters such as the specific credentials for a particular wireless protocol, such as a WiMAX protocol. It may also include operator specific credentials including the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of a bootstrap server in the femtocell network service provider (NSP) |
| 4 | US7855977B2 | Alarming in a femto cell network | To efficiently gauging performance of a femto cell network through generation of alarms based on performance rules for aggregated operational data of multiple femto cell access points. | System(s) and method(s) to monitor operation quality of a femto cell network is provided. Operational data received from deployed femto cell access points are aggregated and monitored; aggregation and monitoring take place within a femto cell network platform. |
| 5 | US20100309790A1 | Femto base stations and methods for operating the same | A major obstacle to using GPS systems to determine and track the location of a femto base station is presented when the femto base station is located indoors because satellite signal penetration indoors is highly unreliable. | The femto base stations and methods to suppress the need for external global positioning system (GPS) antennas and cables, while continually enabling a network service provider to obtain desired position information. It also provide user with the flexibility to place the femto base station at the location of his/her choice within the home or business regardless of GPS signal strength. |
| 6 | US20100285812A1 | Call admission priority control determination device and mobile wireless communication system | When more than one terminal is present in the same cell and these terminals communicate with one base station, the wireless resources of that base station are shared among the plural terminals. As a result, the communication rate becomes lower than when communication is performed by only one terminal. Thus, there is a problem that the use of the femtocell base station by other users deteriorates the quality of communication by specified terminal users such as the femtocell base station administrator. | It can be solved by a call admission priority control determination device including a registration table containing base station ID numbers of base stations and an ID number of a high-priority first terminal, and a call admission determination unit that determines call admission with reference to the registration table, wherein, when a connection request or a switching-over request for a third terminal has been received from a base station control device, the call admission determination unit, on the basis of this request, references the registration table and determines whether or not call admission for the third terminal is to be permitted. |
| 7 | US20100279704A1 | Method for controlling access to a mobile communications network | Current 3G redirection features do not allow for redirection of UE’s from a first cell to another cell operating at the same frequency as the first cell. Therefore, if the 3G femtocell is operating at the same frequency as a neighboring 3G RAT or macrocell, then the current redirection mechanism cannot be used for balancing the load. This is due to interference between cells. | For particular femtocells which have reached or are nearing full capacity, a UE such as a mobile telephone or mobile communication device can be redirected from a 3G femtocell to another macrocell operating at the same or different frequency as the femtocell (access point). This provides improved communications for existing users within the femtocell, as well as for new users whose communications have been redirected to another cell. |
| 8 | US20100267386A1 | Methods and apparatus for facilitating handoff between a femtocell base station and a cellular base station | The resources of a wireless communication system (e.g., bandwidth and transmit power) may be shared among multiple subscriber stations. A variety of multiple access techniques are known, including CDMA, TDMA, FDMA, OFDMA, SC-FDMA etc. Benefits may be realized by improved methods and apparatus related to the operation of wireless communication systems. | A method to facilitate femtocell-to-cellular base station handoff is provided. The femtocell base station may receive a neighbor list from the cellular base station. The neighbor list may include information about other cellular base stations. The femtocell base station may broadcast the neighbor list to subscriber stations that are located within a coverage area of the femtocell base station. |
| 9 | US20100177695A1 | Technique for interference mitigation using mobile station signaling | MS cannot access the neighboring FBS because the neighboring FBS is a CSG FBS and therefore does not allow access to an unauthorized MS, except for an emergency service. Therefore, the MS falls into a black hole in the network, even though the MS is located within the service coverage area of the FBS it is authorized to receive service from. In worse scenario, the MS is prohibited from sending any signal to the neighboring FBS since the neighboring FBS is a CSG FBS | A method to operate an MS for Interference Mitigation (IM) in a wireless communication system including a plurality of Closed Subscriber Group (CSG) FBSs is provided. The method includes determining if the MS cannot access a first CSG FBS due to interference from a second CSG FBS, the first CSG FBS being a CSG FBS that the MS is authorized to receive service from and the second CSG FBS being a CSG FBS that the MS is not authorized to receive service from, and in the case when MS cannot access the first CSG FBS due to interference received from the second CSG FBS, transmitting an IM-Signal to the second CSG FBS requesting that the second CSG FBS mitigate the interference to the MS |
| 10 | JP2010157807A | Communication system, femto cell base station, authentication device, communication method, and communication program | To provide a communication system for assuring communication security in communication between a femto cell base station and an UE. | Communication system is presented which includes: the UE (User Equipment) and an HLR (Home Location Register) to be used in an IMS (IP Multimedia subsystem) network; and the femto cell base station (Femto AP) organizing a prescribed communication area. The femto cell base station (Femto AP) is a communication system existing between the UE and the HLR, to keep the UE confidential through the use of authentication information corresponding to the UE obtained from the HLR when the UE is authenticated. |
| 11 | US20100165957A1 | Providing a cellular network with connectivity to a different network | An access point in a cellular network for providing a cellular device with network connectivity to a different network. | A System is provided for use in wireless communication which includes a first device communicating via a first protocol in a first network, a cellular device communicating via a second protocol in a cellular network, the second protocol being incompatible with the first protocol, and an access point in the cellular network, the access point being accessible by the cellular device and being configured to enable communication between the first device and the cellular device. |
| 12 | US20100135201A1 | Registration notification for mobile device management | To notification of registration of a mobile device within femto coverage area for device content management. | A method is presented in which notification is conveyed to a network component or platform that manages firmware content(s) updates when a mobile device for which an update is available, hands off from wireless macro network coverage onto a femto cell coverage. The notification is delivered in response to a firmware update notification delivered to a component that administers location of the mobile device, or an update flag delivered to a femto access point that can provide femto coverage to the mobile device. |
| 13 | US20100130212A1 | Femto cell handover in wireless communications | Techniques and systems for performing handover of a mobile station between a cellular wireless network and a private cell or private network. | Presented a techniques and systems for performing handover of a mobile station between a cellular wireless network and a private cell or private network which includes operating a macrocell base station to provide wireless service to mobile stations, determining a candidate group of one or more femtocell base station candidates based at least on respective one or more proximities to the macrocell base station to perform a handover of a mobile station that is being served by the macrocell base station, causing the mobile station to take measurements of signals from one or more base stations identified by the candidate group, and selecting a target femtocell base station from the candidate group for the handover based on the measurements. |
| 14 | GB2461845A | Femtocell basestation scrambling code selection | The mobile network operator may allocate only a small number of scrambling codes for use by all of the deployed femtocell basestations, and in fact it is possible that there may be only one scrambling code allocated for use by all of the femtocell basestations in an operator’s network, and so there is a possibility that two femtocell basestations that are located very close together may need to use the same scrambling code. | A method for reducing the possibility of interference between femtocell basestations that are located very close together may need to use the same scrambling code which includes method of selecting a scrambling code, for use in a basestation of a cellular communications network, the method comprising: receiving from a management system a list comprising at least one allowed scrambling code for femtocell basestations; and detecting, in information broadcast by at least one macrocell basestation, at least one allowed scrambling code available in an area containing the basestation. |
| 15 | US20090286540A1 | Femtocell architecture for information management | Congestion in the backhaul network and delays during communication increases because an increase in the number of devices attached to a femto cell, the traffic on the backhaul network of the femto cell can increase significantly | The method presented can facilitate reduction in backhaul network traffic and communication delay by employing an enterprise femto architecture. The enterprise femto architecture employs a routing platform to connect multiple femtos access points to a common femto gateway to generate a mesh network. |
| 16 | EP2112854A1 | Access control method for cellular networks comprising femto-cells | It is not necessary that the femto system may know at each time the cell locations of all user equipments camping in its area because it will be unable to track those user terminals entering the femto-cell while in the Idle Mode, and also taking into account the fact that up to 6 minutes might be necessary for the user terminal to trigger its periodic location update. Because of this it would not be possible to distribute paging messages from the Core Network to individual femto-cells without running the risk that paging may not be received by the user equipment addressed thereby. | A method is provided to control access of user terminals to a femto system which includes Non Access Stratum (NAS) Mobility Management (MM) messages as well as Access Stratum (AS) Radio Resource Control (RRC) messages. |
| 17 | US20090253421A1 | Local network management of femtocells | Femtocells could suffer from interference problems without unique spectrum for the femtocell underlay network such as, in a high-rise apartment complex environment, a number of femtocells may be placed near each other, and may be separated only by the floor and/or walls of adjacent apartment units. If these femtocells operate on the same channel, then one femtocell may interfere with the operation of the other femtocell, and vice-versa. | A method to minimize signal interference within a wireless network, the wireless network including a controller communicatively coupled to at least one femtocell, wherein the femtocell is operative to wirelessly transmit and receive data, the method includes: using a portable electronic device to collect signal environment data; analyzing the collected signal environment data; and based on the analyzed signal environment data, commanding the at least one femtocell to alter at least one signal transmission characteristic. |
| 18 | GB2456503A | Using global cell identifier for handover in a combined femto-cell/macro-cell environment | When large number of femto cells compared to the number of macro cells is present, it is not possible to ensure that all the femto cells within the coverage area of a macro cell have individual and different frequencies and scrambling codes. So in a combined femto cell-macro cell environment, the macro cell RNC will be unable to determine, from the measurement report received from the UE, which cell (either a femto cell or macro cell) was measured. | A method is provided which includes a network element for a cellular communication system, network element comprises a receiver for receiving a message that comprises a measurement report from a wireless communication unit. The network element further comprises signal processing logic, operably coupled to the receiver, for processing the received measurement report and extracting a global cell identifier therefrom, so the inventive concept provides an improvement to the use of measurement reports, which may be used to facilitate handover between cells in a cellular communication system. |
Article Analysis
| S. No. | Title | Publication Date | Journal/Conference | Dolcera Summary |
| 1 | Cognitive Femtocell | Mar. 2011 | IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine | Because of the fact that femtocells can access a resource, sufficiently and locally, to known users with higher throughput, considerable attention has been devoted to the potential cognitive femtocell to allow for higher capacity and intelligent coverage, with guaranteed quality of service (QoS) for future indoor service. Cognitive femtocell is presented as a solution for spectrum-scarcity problems and local-convergence demands for indoor network applications. To control the data packet delivery between the macrocell and cognitive femtocell, A developed gateway broadband router based on novel cross-layer management optimization is used. |
| 2 | Interference Analysis for Femtocell Deployment in OFDMA Systems Based on Fractional Frequency Reuse | Mar. 2011 | Communications IEEE Letters | A method of optimal power allocation for femtocells with different orthogonal subbands, based on analysis of macrocell interferences is presented. |
| 3 | On-Demand Resource-Sharing Mechanism Design in Two-Tier OFDMA Femtocell Networks | Mar. 2011 | IEEE Vehicular Technology Society | Discussed two main design issues in orthogonal frequency-division multiple-access (OFDMA) femtocell networks, i.e., resource sharing and femtocell access control. More comprehensive perspective on self-organizing femtocell networks, where users optimize their performance in a distributed manner is presented. |
| 4 | Open vs. Closed Access Femtocells in the Uplink | Dec. 2010 | IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications | Since open access deployment provides an inexpensive way to expand their network capabilities, so it would be preferred by the network operator whereas the femtocell owner would prefer closed access, in order to keep the femtocell’s capacity and backhaul to himself, but best approach depends heavily on whether the multiple access scheme is orthogonal (TDMA or OFDMA, per subband) or non-orthogonal (CDMA) |
| 5 | Robust Transmission and Interference Management For Femtocells with Unreliable Network Access | Dec. 2010 | IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications | Since each femtocell is served by a home base station (HBS) that is connected to the macrocell base station (BS) via an unreliable network access link, such as DSL followed by the Internet, A scenario with a single macrocell and a single femtocell is presented, and is then extended to include multiple macrocells and femtocells, both with standard single-cell processing and with multicell processing (or network MIMO). Two main issues are presented regarding uplink channel: (i) Interference management between femto and macrocells; (ii) Robustness to uncertainties on the quality of the femtocell (HBSto-BS) access link. |
Top Cited Patents
| S. No. | Patent/Publication No. | Publication Date (mm/dd/yy) |
Assignee/Applicant | Title | Citation Count |
| 1 | US20070097939A1 | 05/03/07 | Ericsson | Automatic configuration of pico radio base station | 60 |
| 2 | US20070254620A1 | 11/01/07 | Ericsson | Dynamic building of monitored set | 33 |
| 3 | US20080132239A1 | 06/05/08 | Kineto Wireless | Method and apparatus to enable hand-in for femtocells | 20 |
| 4 | US20050144647A1 | 06/30/05 | Mordechai Zussman (Inventor) | Wireless provider monitoring of catv segment | 17 |
| 5 | US20070270152A1 | 11/22/07 | Ericsson | Access control in a mobile communication system | 16 |
| 6 | US20080261602A1 | 10/23/08 | Qualcomm | Backhaul network for femto base stations | 12 |
| 7 | US20080076425A1 | 03/27/08 | Kineto Wireless | Method and apparatus for resource management | 11 |
| 8 | US20080244148A1 | 10/02/08 | Go2Call.com | VoIP enabled femtocell with a USB transceiver station | 8 |
| 9 | US20090040972A1 | 02/12/09 | Julius Robson (Inventor) | Radio resource allocation for cellular wireless networks | 7 |
| 10 | US20080305801A1 | 12/11/08 | Lucent Technologies | Method and apparatus to allow hand-off from a macrocell to a femtocell | 7 |
Top Cited Articles
| S. No. | Title | Publication Date | Journal/Conference | Citations Count |
| 1 | Femtocell networks: a survey | Sep. 2008 | IEEE Communications Magazine | 272 |
| 2 | Performance of Macro- and Co-Channel Femtocells in a Hierarchical Cell Structure | Sep. 2007 | IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, 2007 | 93 |
| 3 | Effects of User-Deployed, Co-Channel Femtocells on the Call Drop Probability in a Residential Scenario | Sep. 2007 | IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, 2007 | 75 |
| 4 | Uplink capacity and interference avoidance for two-tier femtocell networks | Jul. 2009 | IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications | 62 |
| 5 | OFDMA femtocells: A roadmap on interference avoidance | Sep. 2009 | IEEE Communications Magazine | 55 |
| 6 | WiMAX femtocells: a perspective on network architecture, capacity, and coverage | Oct. 2008 | IEEE Communications Magazine | 55 |
| 7 | An overview of the femtocell concept | May. 2008 | Bell Labs Technical Journal | 53 |
| 8 | Self-optimization of coverage for femtocell deployments | Apr. 2008 | Wireless Telecommunications Symposium, 2008 | 49 |
| 9 | Power control in two-tier femtocell networks | Aug. 2008 | IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications | 34 |
| 10 | Interference management and performance analysis of UMTS/HSPA+ femtocells | Sep. 2009 | IEEE Communications Magazine | 26 |
Patent Ranking
| S.no | Patent/Publication No. | US Class (primary) | Title | Publication Year | Priority Year(s) | Legal Status | Rank |
| 1 | US7855983B2 | 370280 | Time Division Duplex Front End Module | 2010 | 2006 | 2007 | 2007 | 2008 | Patented Case | 3 |
| 2 | US7613444B2 | 455403 | Dynamic Building Of Monitored Set | 2009 | 2006 | Patented Case | 1 |
| 3 | US20110105129A1 | 455443 | Femtocell Search Method For Macro To Femto Handover | 2011 | 2008 | 2008 | 2010 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 2 |
| 4 | US20110047011A1 | 7050141 | Incentives To Optimize The Performance Of Femto Cell Groups | 2011 | 2009 | Docketed New Case - Ready for Examination | 2 |
Disclaimer: Patent ranking has been done according to the following logic:
- Rank-1: Granted + Femtocell related (claims)
- Rank-2: Published + Femtocell related (claims)
- Rank-3: Femtocell related (Full spec )
- Rank-4: May be relevant
- Rank-5: Abandoned or Expired
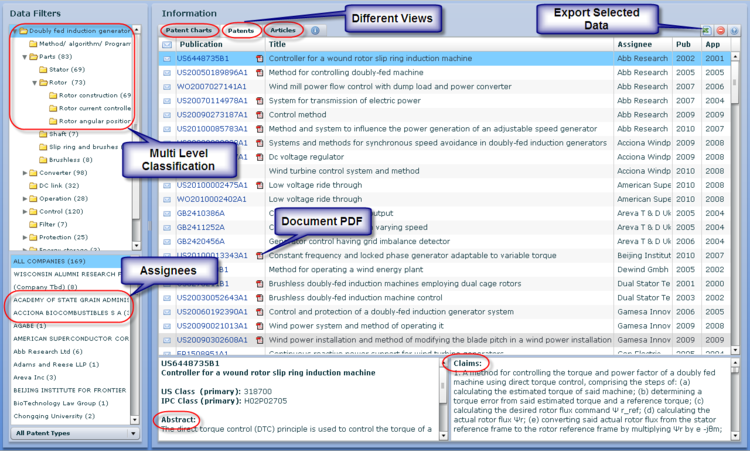
Dolcera Dashboard
Dashboard Links
The Dashboard is Dolcera's visualization platform to present the organized patent landscape
- Best viewed in Internet explorer 6 and higher versions
- To view dashboard you would require a flash player. Kindly install a flash player if its not installed in your system
| Femtocell-Network Category - Dashboard | |
| Femtocell-Problem Solution Mapping of Handover Node- Dashboard |
- Note1: Use the following credentials to view the dashboard 1.1
- Username: demo@dolcera.com
- Password: demo123
- Note2: A total of 100 patents were considered for the creation of the sample dashboard
Products
| S. No. | Company | Product | Specification |
| 1 | AT&T | Power Supply: 100-120 VAC, 15 W; 12 VDC, 1.25 A Output. Status Indicators: Power, Ethernet, GPS, Computer, 3G. Dimensions (H x D x W): 8.5 in.x6.3 in.x1.5 in. (at top), 4 in. (at legs). Unit Weight: 1 lb 2 ounces (AC power adapter not included). Ambient Temperature Range: 0° to 38°C | |
| 2 | Cisco | Front panel indicators: Power, Ethernet, GPS, PC, 3G. GPS antenna extender: Optional external GPS antenna input. Ethernet connection: RJ-45, WAN connection with broadband modem. PC connection: RJ-45, LAN connection with PC or network router. Reboot button: Restarts device initialization and authentication. UMTS bands: 1900 MHz and 850 MHz (Bands 2 and 5). Output power: 5mW. HSDPA aggregate throughput: Up to 3.6 Mbps. AC power adapter: Input: 90-120VAC; Maximum output: 12V, 1.67A, 20W. Temperature range: 0° to 45°C (32° to 113°F). Dimensions: 7.0 in x 8.0 in. x 2.0 in. Weight: 1.0 lb | |
| 3 | AirWalk Communications | Dual Mode: EVDO and 1xRTT, Ethernet backhaul, Self-optimizing, Plug-and-play installation, Single band 800/1900 MHz, 2G and 3G handset compatibility, IOS/SIP interface | |
| 4 | AirWalk Communications | Dual-mode: CDMA 1xRTT and EVDO Rev. A (Rev B+ capable) in one device, Integrated BTS, BSC, RN, RNC, PCF and O&M, Self-optimizing, Plug-and-play installation, Advanced handoff capability (clustering), 10/100 Ethernet backhaul, Single band 450/800/1900 MHz, 2G/3G handset compatibility, IOS or SIP/IMS core network compatibility | |
| 5 | Airvana | Simultaneous 1xRTT and EV-DO Rev-A, Flat IP-based architecture, SIP/IMS Core Network Interface, Plug-and-Play Install, Automated Network Planner, Comprehensive Remote Management, Compatible with standard CDMA 1xRTT and EV-DO Rev-A handsets, Ethernet Backhaul | |
| 6 | Airvana | RF output power: 20 dBm, Supports 4 Simultaneous AMR Channels (voice calls), 7.2 Mbps HSDPA & 1.5 Mbps HSUPA, Range 50m to 200m, Ethernet Backhaul | |
| 7 | Samsung | RF output power: Up to 50mW, System Capacity: 1carrier / Omni, Traffic Channel: Up to 4 simultaneous users, Air Interface: CDMA2000 1X, Frequency: 1.9GHz (SCS-26UC2), 800MHz (SCS-26UC3), Dual Band (SCS-26UC4), Input Power: 00~250VAC, Network Interface: 10/100 Base-T Ethernet, Volume: 95 in3 (1.5 Liters), Weight: 1.41 lb (640g), Operating Temperature: 32°F to 113°F (0°C to 45°C), Dimension: 6.1 x 8.2 x 1.9 inch (154 x 208 x 47 mm, HWD) | |
| 8 | Samsung | RF Output: Up to 20mW, System Capacity: 1carrier / Omni, Traffic Channel: Up to 4 simultaneous users, Air Interface: WCDMA / HSPA, Frequency: 2.1GHz, Input Power: 100~240VAC, Network Interface: 10/100 Base-T Ethernet, Volume: 1.4 Liters, Weight: 600g, Operating Temperature: 0°C to 45°C, Dimension: 185 x 210 x 36 mm (HWD) | |
| 9 | ip.access | RF output power: 5mW (+7dBm), UMTS bands: 1,4,2/5, Simultaneous users: 8, Electrical power: <8W, External antennas: No, Oscillator: VCTCXO, NTP: Time stamp & sync, Temp. range: 0° to 40°C, Dimensions(mm): 193x171x53 | |
| 10 | Huawei | RF output power: 20mW, Traffic Channel: Up to 4 simultaneous users | |
| 11 | Argela | Radio frequency: UMTS FDD band I support, Transmit power: 23 dBm (200 mW) maximum, Cell radius: 200m maximum, Maximum active UEs: 8, Access control: Closed, Open, or Hybrid, UMTS services: 12.2 kbps AMR for voice, 64 kbps video (128 kbps can be supported), PS data services at upto 384 kbps, HSDPA 14 Mbps downlink (limited by DSL speed), HSUPA 5.7 Mbps uplink (limited by DSL speed), Physical characteristics: Max power consumption of 10W during normal operation, 18cm x 11cm x 2.5cm, 12V DC supply, Weight 400g, RJ-45 10/100 Ethernet connection to the DSL CPE |
Market Research
Mobile Communication Problems
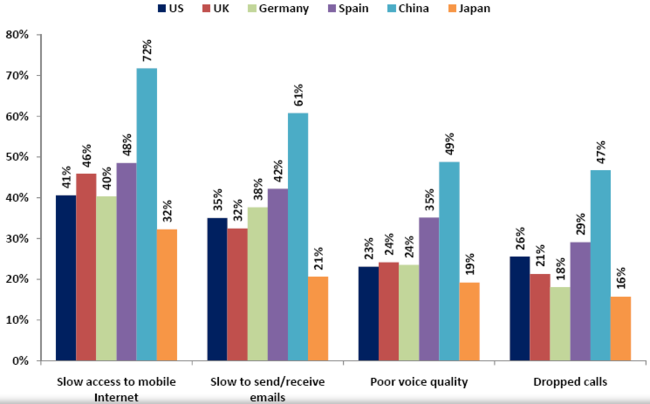
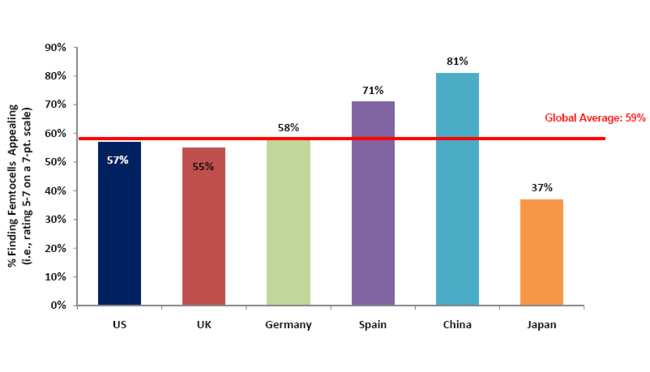
- Parks Associates, commissioned by the Femto Forum, has conducted this custom consumer research in six nations: the U.S., the U.K., Germany, Spain, China, and Japan. The following chart illustrates the problem associated with mobile communication, from which we can conclude that China has severe problems in mobile based services.
Source: Parks Associates
Demand of Femtocells
- From the above chart we can see that China has severe problems in mobile based services, therefore, the demand of femtocells is more in China.
Source: Parks Associates
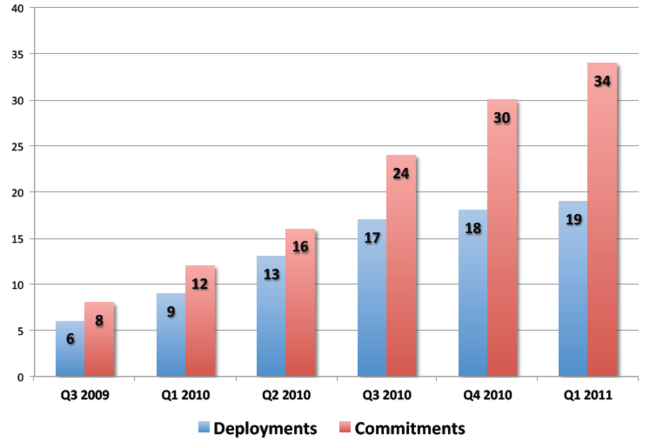
Deployment and Commitments of Femtocell Service
- This chart exemplifies a historical representation of deployments and commitments, both of which have increased almost 300% within a year.
Source:Informa Telecoms & Media
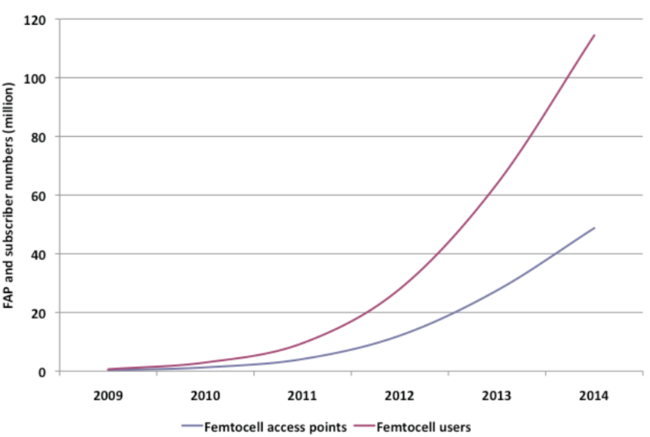
Market Forecast
- The following chart exemplifies Informa’s forecasts (January 2010) for femtocell access point shipments and users.
Source:Informa Telecoms & Media
The following table provides a summary of publicly announced statements, sorted by reverse chronological order. The table is followed by more information regarding each statement:
- Strategy Analytics expects femtocell access point shipments to reach 2 million during 2010 (Strategy Analytics – November 2010).
- ABI research expects 1 million femtocells to have been shipped by the end of 2010,increasing to 54 million femtocell shipments during 2015. ABI research estimates that 1.3 million femtocells have been shipped to operators from vendors during 2010. The estimate for femtocell shipments for 2011 is 3.8 million and 70 million for 2015(ABI Research – September 2010).
- IDate has updated its femtocell market forecasts, with 11.7 million femtocell access point shipments during 2013, increasing to 23 million during 2014 (iDate – September 2010).
- Alcatel Lucent has performed research on consumer attitudes to a variety of femtocell marketing propositions and forecasts more than 34 million femtocell users in the US, UK, Germany, Singapore and Taiwan by 2014, at which point the market will be worth over €6 billion (Alcatel Lucent– September 2010)
- In-Stat has published updated femtocell forecasts, and expects that worldwide annual enterprise femtocell revenue CAGR will be 125.7% from 2009-2014 (In-Stat - September 2010).
- Dell’Oro expects estimates 1 million femtocell access points to ship this year, reaching 62 million during 2014, more than 80% of which will be WCDMA femtocells (Dell’Oro - August 2010).
- iSuppli forecasts that shipments will rise to 1.9 million during 2010, up from 571,000 in 2009. A period of expansion then will follow, with shipments reaching 7.2m units in 2011, up 289% from 2010. Shipments are forecast to rise by 232% to reach 23.9m units in 2012 and by 657% to hit 39.6m units in 2013. (iSuppli - March 2010).
- GIA projects the femtocell market to surpass 75.8 million by the year 2015, driven by the ongoing migration of mobile operators from smaller access points to large base stations. (Global Industry Analysts - March 2010).
Source:Informa Telecoms & Media
Key Findings
Note: Total 864 Sample patents were taken into consideration for analysis (Data upto 8th March 2011).
- Qualcomm, Samsung and NEC are the major players in femtocells technology
- Key patents in the femtocells are held by Ericsson, Kineto Wireless and Qualcomm.
- Patenting activity has seen a very high growth rate in the last two years.
- US and WO are very active in femtocell technology research.
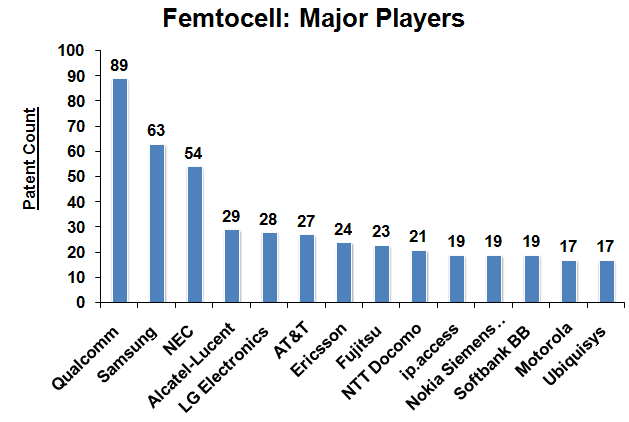
Major Players
- The following chart illustrates the Major Players in femtocells technology from which it can be concluded that the Qualcomm, Samsung and NEC are the major players in femtocells technology.
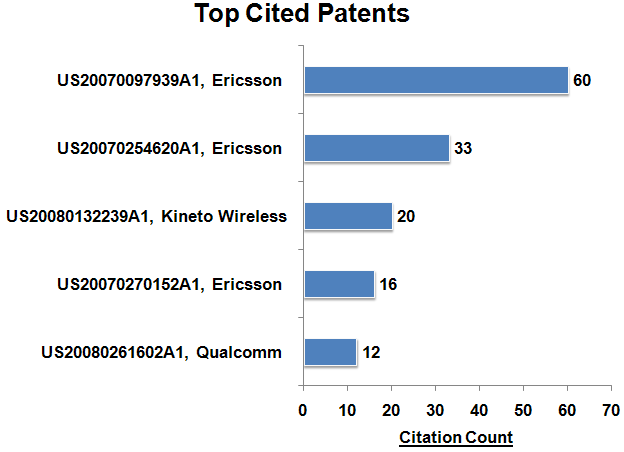
Key Patents
- The following chart illustrates the Key Patents in femtocells technology from which it can be concluded that the key patents in the femtocells are held by Ericsson, Kineto Wireless and Qualcomm.
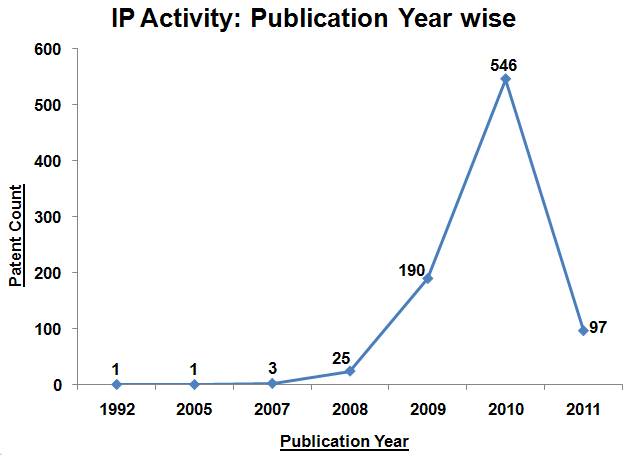
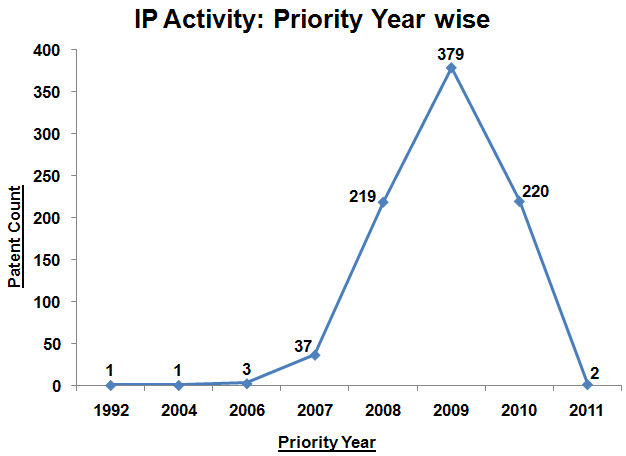
IP Activity
- The following charts illustrate the Patent Publication/Priority activity in previous years from which it can be concluded that the Patenting activity has seen a very high growth rate since 2008.
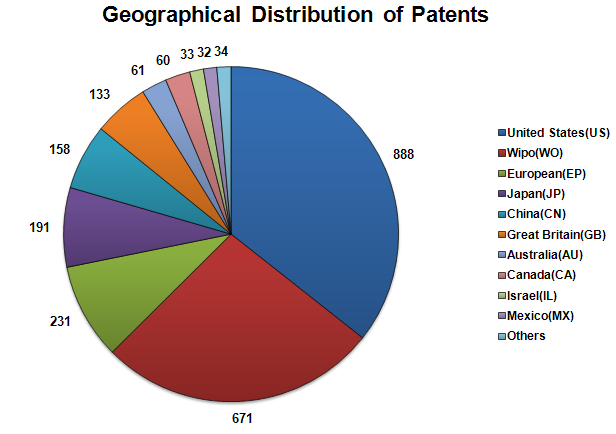
Geographical Activity
- The following chart illustrates the Geographical Distribution of patents from which it can be concluded that the US and WO are very active in femtocell technology research.
- Others includes 13 Patents from Germany(DE), 8 Patents from South Korea(KR), 6 Patents from Austria(AT), 5 Patents from France(FR) and 2 Patents from Brazil(BR).
Market Player Analysis
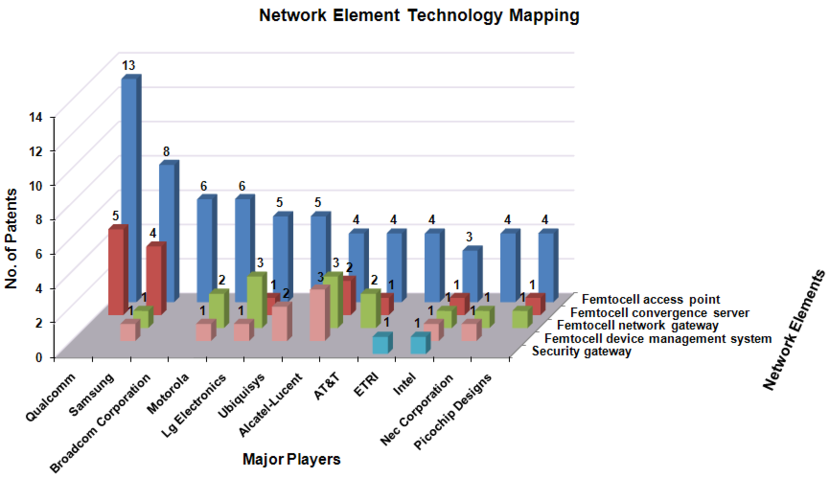
Network Element Technology Mapping
The following chart illustrates Network element technology mapping with top market players and drawn based on 100 sample patents as given on the dashboard from which it can be concluded that significant work is being done on Femtocell access point.
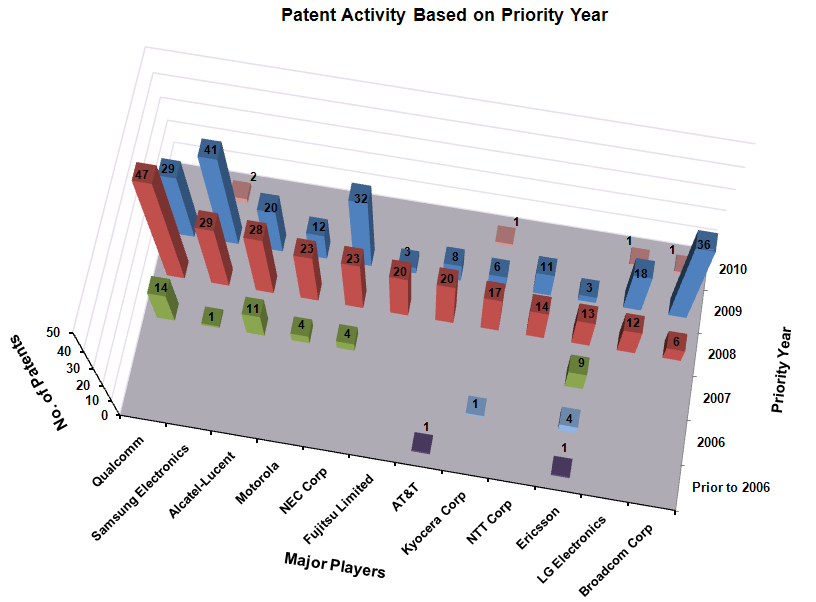
Patent Activity Based on Priority Year
The following chart illustrates Patent/Publication activity year by year for top market players from which it can be concluded that significant research activity has taken place in the years 2008 and 2009
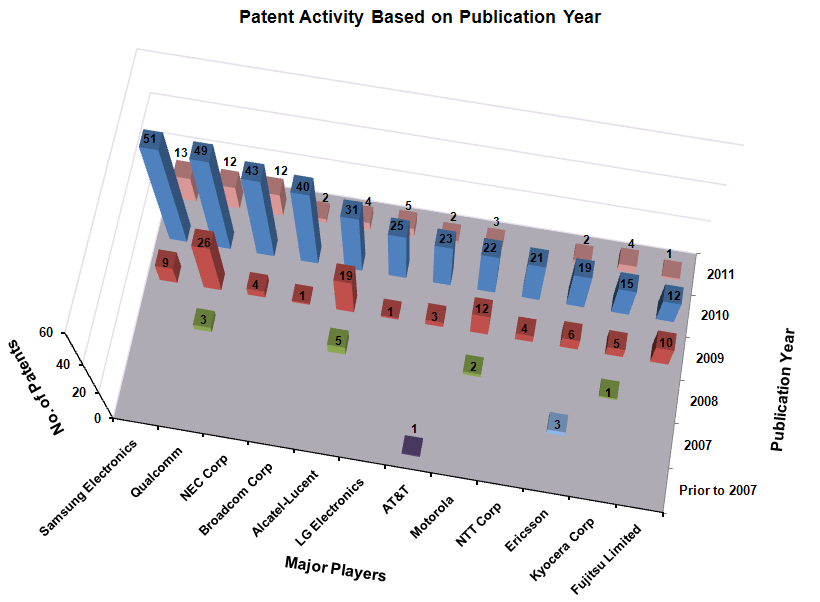
Patent Activity Based on Publication Year
The following chart illustrates Patent/Publication activity year by year for top market players from which it can be concluded that significant research activity has been published from 2009 onwards.
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs
References
Contact Dolcera
| Samir Raiyani |
|---|
| Email: info@dolcera.com |
| Phone: +1-650-269-7952 |